How to operate a drone safely and effectively opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering pre-flight checks, control techniques, flight planning, camera operation, maintenance, and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of maneuvering your drone, ensuring both safe and successful flights.
From understanding basic controls to mastering advanced techniques like waypoint navigation and cinematic shots, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and achieve professional results. Whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this guide offers valuable insights and practical advice.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves checking various components and verifying system functionality to mitigate potential risks.
Pre-flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight inspections are paramount for preventing accidents and ensuring the drone’s optimal performance. Overlooking even minor issues can lead to malfunctions mid-flight, potentially causing damage to the drone, property, or even injury.
Comprehensive Pre-flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should be followed religiously. This checklist ensures all critical systems are functioning correctly before initiating flight.
- Battery Check: Verify battery charge level and ensure it’s fully charged or within the recommended operational range. Check for any physical damage to the battery.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine propellers for any cracks, bends, or damage. Ensure they are securely fastened to the motors.
- GPS Signal Verification: Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. The number of satellites locked should be sufficient for stable flight (usually 5 or more).
- Gimbal Check: Ensure the gimbal moves smoothly and is correctly calibrated. Check for any obstructions.
- Camera Functionality: Test the camera to ensure it’s functioning correctly and capturing clear images or videos.
- Radio Control Connection: Verify a strong and stable connection between the drone and the remote controller.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts, damage, or debris.
Common Pre-flight Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Low Battery | Charge the battery fully. Consider carrying spare batteries. |
| Damaged Propeller | Replace the damaged propeller. |
| Weak GPS Signal | Move to an area with better GPS reception, away from buildings or obstructions. |
| Gimbal Malfunction | Recalibrate the gimbal. If the problem persists, seek professional assistance. |
Safe Power-On Procedure
- Ensure the drone is placed on a stable, level surface away from obstacles.
- Power on the remote controller first.
- Power on the drone’s battery. Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Verify all systems are operational before proceeding to takeoff.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is crucial for safe and efficient flight. This section covers basic controls, different interfaces, and techniques for smooth maneuvering.
Basic Drone Controls
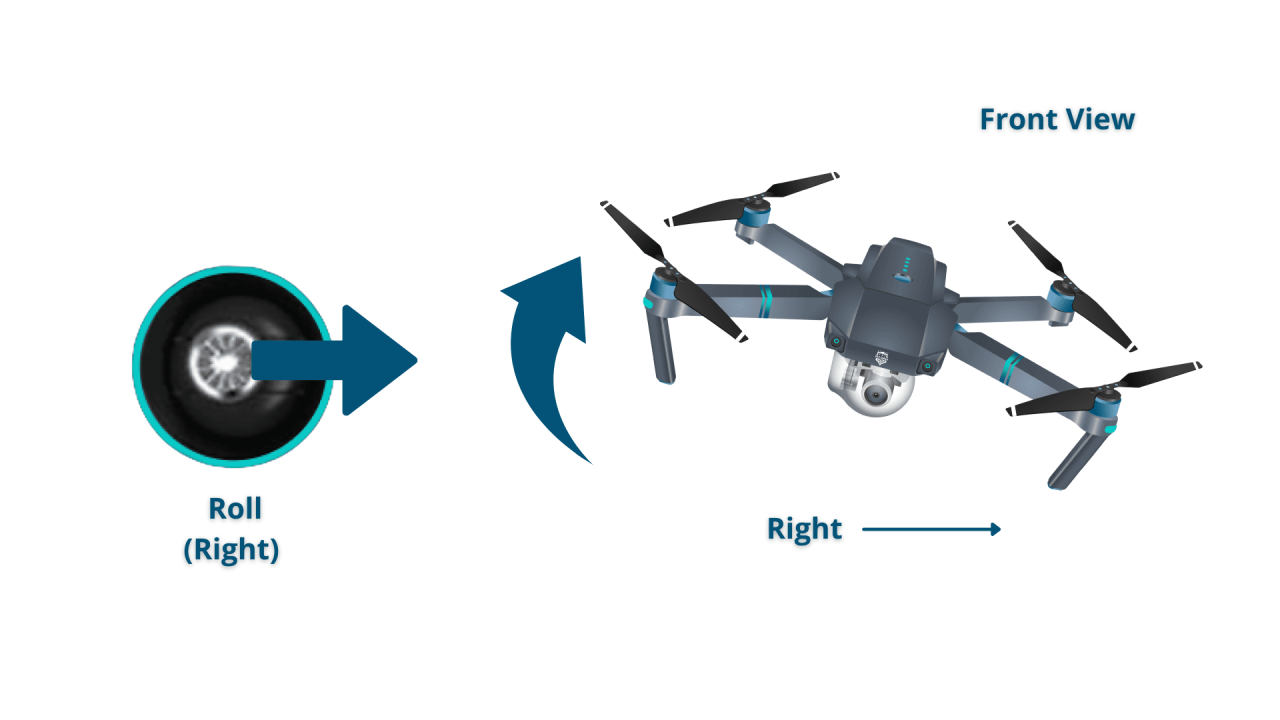
Most drones use two joysticks for controlling flight. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls roll (tilting left/right) and pitch (tilting forward/backward). Buttons on the controller are used for various functions, such as camera control, returning to home, and emergency stops.
Drone Control Interfaces
Different drone manufacturers may offer slightly varying control interfaces. Some offer customizable settings and features, allowing pilots to tailor the experience to their preferences. However, the fundamental principles of controlling altitude, direction, and camera remain consistent.
Altitude Hold and GPS Stabilization
Altitude hold uses sensors and GPS data to maintain a consistent altitude, simplifying flight and reducing the need for constant altitude adjustments. GPS stabilization enhances stability by using GPS data to counteract wind and other external forces.
Tips for Smooth and Precise Maneuvering
Smooth and precise drone maneuvering requires practice and understanding of the drone’s responsiveness. Start with slow, deliberate movements, gradually increasing speed and complexity as you gain experience. Avoid abrupt control inputs.
Flying in Different Wind Conditions
- Low Wind: Maintain a stable altitude and direction, making small adjustments as needed.
- Moderate Wind: Increase the drone’s responsiveness settings and use more precise control inputs to counteract wind gusts.
- High Wind: Avoid flying in high winds. If necessary, make short flights and return quickly to a sheltered location.
Taking Off, Landing, and Emergency Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents and damage. Understanding emergency procedures is crucial for handling unexpected situations.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
- Ensure the area is clear of obstacles and people.
- Check for any wind conditions.
- Slowly lift the drone vertically using the left joystick.
- Maintain a steady ascent until reaching the desired altitude.
Smooth and Controlled Landing
- Gradually descend the drone using the left joystick.
- Maintain a slow and steady descent.
- Once the drone is close to the ground, gently lower it until it touches down.
- Turn off the drone and controller.
Potential Hazards During Takeoff and Landing
Obstacles, wind gusts, and uneven terrain can pose significant risks during takeoff and landing. Careful pre-flight planning and choosing a suitable location can mitigate these hazards.
Emergency Procedures Flowchart (Descriptive Text)
A flowchart would visually represent the decision-making process in an emergency. If signal loss occurs, the drone will initiate its return-to-home function. If a malfunction occurs, attempt to regain control, then initiate the return-to-home function if unsuccessful. If the drone becomes unresponsive, the emergency stop button should be used. The flowchart would visually show this sequence of actions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception.
- Low Battery: Land immediately and charge the battery.
- Motor Failure: Land immediately and inspect the motor.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or seek professional assistance.
- Controller Disconnection: Check the controller’s batteries and connection.
Flight Planning and Navigation
Flight planning is essential for safe and efficient drone operations. This involves determining flight time, identifying restricted airspace, and planning the flight path.
Importance of Flight Planning
Flight planning helps ensure a safe and successful flight by considering factors such as battery life, weather conditions, and airspace restrictions. It allows for a more organized and efficient flight operation.
Calculating Flight Time
Flight time is calculated by dividing the battery’s capacity (in mAh) by the drone’s power consumption (in mAh/minute). For example, a drone with a 5000 mAh battery and a 100 mAh/minute consumption rate has a potential flight time of 50 minutes (5000 mAh / 100 mAh/minute). This is a theoretical maximum; actual flight time is affected by factors such as wind and camera usage.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including legal considerations and practical flying techniques, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and the integrity of airspace.
Identifying and Avoiding Restricted Airspace
Before each flight, it’s crucial to check for restricted airspace using online resources or mobile applications. This ensures compliance with regulations and avoids potential legal issues or conflicts with other aircraft.
Using Waypoints and Pre-programmed Flight Paths
Many drones allow users to set waypoints (specific geographic coordinates) to create pre-programmed flight paths. This enables automated flights along a desired route, simplifying complex aerial photography or inspection tasks.
Typical Flight Path Planning Process (Descriptive Text), How to operate a drone
A typical flight path planning process would begin with identifying the desired area for aerial coverage. Waypoints would then be strategically placed to cover this area, considering factors such as altitude, wind conditions, and potential obstacles. The flight path would be visualized on a map or screen, allowing for adjustments before initiating the flight.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Drone cameras offer incredible capabilities for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera features and settings is essential for achieving optimal image quality.
Typical Drone Camera Features
Typical drone cameras offer various features, including high resolution, adjustable aperture, and various shooting modes. Resolution varies depending on the model but generally ranges from 12MP to over 48MP for still images. Video recording capabilities often include 4K resolution at high frame rates.
Different Shooting Modes

Most drones support multiple shooting modes, including photo, video, timelapse, and even slow-motion video. Each mode offers unique capabilities for capturing different types of aerial content.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Adjusting camera settings, such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, is crucial for optimal image quality in various lighting conditions. In bright conditions, lower ISO and faster shutter speeds are often preferred. In low light, higher ISO and slower shutter speeds may be necessary, potentially requiring the use of a tripod or gimbal to mitigate motion blur.
Capturing Professional-Looking Aerial Photos and Videos
Achieving professional-looking aerial photos and videos requires understanding composition, lighting, and post-processing techniques. Utilizing the “rule of thirds,” incorporating leading lines, and paying attention to lighting conditions are key factors for creating visually appealing content. Post-processing tools can further enhance image quality and create specific stylistic effects.
Achieving Specific Photographic Effects
Cinematic shots can be achieved through smooth, controlled movements and careful camera angles. Panoramic views are created by stitching together multiple overlapping images. Understanding camera movement and post-processing techniques is crucial for realizing creative visions.
Drone Maintenance and Storage

Regular maintenance and proper storage are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its optimal performance.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering the art of drone operation takes practice and patience, but the rewards of capturing stunning aerial footage are well worth the effort.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A routine maintenance schedule should include regular inspections of all components, cleaning, and lubrication of moving parts. The frequency of these checks depends on the frequency of use, but monthly checks are recommended for most users.
Cleaning and Storing Drone Components
Drone components should be cleaned gently with a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solutions. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Store the drone and its components in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common problems include propeller damage, battery issues, and gimbal malfunctions. Regular inspections and preventative maintenance can help minimize these issues.
Importance of Regular Battery Maintenance
Proper battery maintenance is crucial for maximizing battery lifespan and preventing potential safety hazards. This includes storing batteries at optimal temperatures and avoiding overcharging or discharging.
Checklist for Proper Drone Storage
- Store the drone in a dry, cool place.
- Keep the drone away from direct sunlight.
- Store batteries separately from the drone in a dedicated storage case.
- Ensure all components are clean and free of debris.
- Protect the drone from physical damage.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone requires adherence to various laws and regulations. Understanding these regulations is crucial for avoiding legal issues and ensuring responsible drone operation.
Key Regulations Governing Drone Operation
Regulations vary by region and country. These regulations typically cover aspects such as registration, licensing, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations. It is crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before operating a drone.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. These permits may be required for commercial use, operation in specific airspace, or for specific types of drones.
Responsible Drone Operation Practices
Responsible drone operation includes respecting privacy, avoiding populated areas, and adhering to all applicable regulations. This ensures safe and considerate use of drones in the public space.
Examples of Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones include areas near airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. These restrictions are in place to ensure safety and prevent interference with other aircraft.
Drone Regulations Comparison (Descriptive Table)
| Country/Region | Registration Requirement | Licensing Requirement | Airspace Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Generally required for commercial use | May be required depending on use | Numerous restrictions near airports and other sensitive locations |
| Canada | Required for all drones weighing over 250g | May be required for commercial use | Restrictions near airports and other sensitive locations |
| European Union | Registration and licensing requirements vary by member state | Generally required for commercial use | Restrictions near airports and other sensitive locations |
| (Add other countries/regions as needed) |
Mastering drone operation is a journey that combines technical understanding with responsible practice. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, from thorough pre-flight checks to meticulous post-flight maintenance, you can ensure both the safety of your drone and those around you. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to regulations are key to becoming a skilled and responsible drone pilot, allowing you to unlock the full potential of this incredible technology.
Popular Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. Calibrate it before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency return-to-home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, try to visually locate the drone and bring it down safely. Report the incident to relevant authorities if necessary.
Can I fly my drone in rain or strong winds?
No, avoid flying in adverse weather conditions. Rain can damage electronics, and strong winds can make controlling the drone extremely difficult and potentially dangerous.
